Units Associated with Gravitational Acceleration
As described on the previous page, acceleration is defined as the time rate of change of the speed of a body. Speed, sometimes incorrectly referred to as velocity, is the distance an object travels divided by the time it took to travel that distance (i.e., meters per second (m/s)). Thus, we can measure the speed of an object by observing the time it takes to travel a known distance.
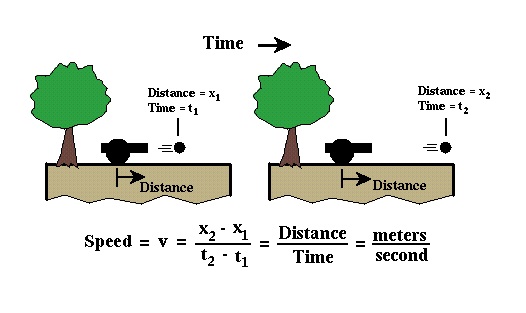
If the speed of the object changes as it travels, then this change in speed with respect to time is referred to as acceleration. Positive acceleration means the object is moving faster with time, and negative acceleration means the object is slowing down with time. Acceleration can be measured by determining the speed of an object at two different times and dividing the speed by the time difference between the two observations. Therefore, the units associated with acceleration is speed (distance per time) divided by time; or distance per time per time, or distance per time squared.
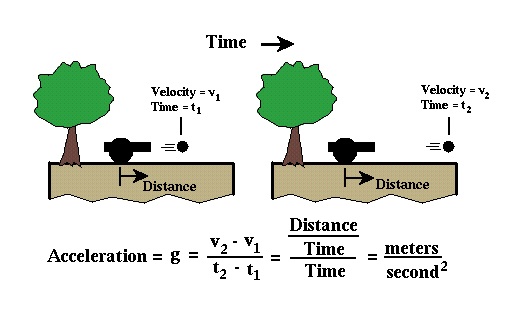
 If an object such as a ball is dropped, it falls under the influence of gravity in such a way that its
speed increases constantly with time. That is, the object accelerates as it falls with constant
acceleration. At sea level, the rate of acceleration is about 9.8 meters per second squared. In gravity
surveying, we will measure variations in the acceleration due to the earth's gravity.
As will be described next, variations in this acceleration can be caused by variations in subsurface
geology.
Acceleration variations due to geology, however, tend to be much smaller than 9.8 meters per
second squared. Thus, a meter per second squared is an inconvenient system of units to use when
discussing gravity surveys.
If an object such as a ball is dropped, it falls under the influence of gravity in such a way that its
speed increases constantly with time. That is, the object accelerates as it falls with constant
acceleration. At sea level, the rate of acceleration is about 9.8 meters per second squared. In gravity
surveying, we will measure variations in the acceleration due to the earth's gravity.
As will be described next, variations in this acceleration can be caused by variations in subsurface
geology.
Acceleration variations due to geology, however, tend to be much smaller than 9.8 meters per
second squared. Thus, a meter per second squared is an inconvenient system of units to use when
discussing gravity surveys.
The units typically used in describing the gravitational acceleration variations observed in exploration gravity surveys are specified in milliGals. A Gal is defined as a centimeter per second squared. Thus, the Earth's gravitational acceleration is approximately 980 Gals. The Gal is named after Galileo Galilei. The milliGal (mgal) is one thousandth of a Gal. In milliGals, the Earth's gravitational acceleration is approximately 980,000.
Gravity
- Overviewpg 12
- -Temporal Based Variations-
- Instrument Driftpg 13
- Tidespg 14
- A Correction Strategy for Instrument Drift and Tidespg 15
- Tidal and Drift Corrections: A Field Procedurepg 16
- Tidal and Drift Corrections: Data Reductionpg 17
- -Spatial Based Variations-
- Latitude Dependent Changes in Gravitational Accelerationpg 18
- Correcting for Latitude Dependent Changespg 19
- Vari. in Gravitational Acceleration Due to Changes in Elevationpg 20
- Accounting for Elevation Vari.: The Free-Air Correctionpg 21
- Variations in Gravity Due to Excess Masspg 22
- Correcting for Excess Mass: The Bouguer Slab Correctionpg 23
- Vari. in Gravity Due to Nearby Topographypg 24
- Terrain Correctionspg 25
- Summary of Gravity Typespg 26